Introduction
Artificial Intelligence has become one of the most influential technologies of our time, and two terms often associated with it are machine learning and deep learning. While many people use them interchangeably, they represent different approaches with unique capabilities. Understanding the difference between machine learning and deep learning helps businesses and individuals make smarter decisions when applying AI to solve real-world problems.
What is Machine Learning?
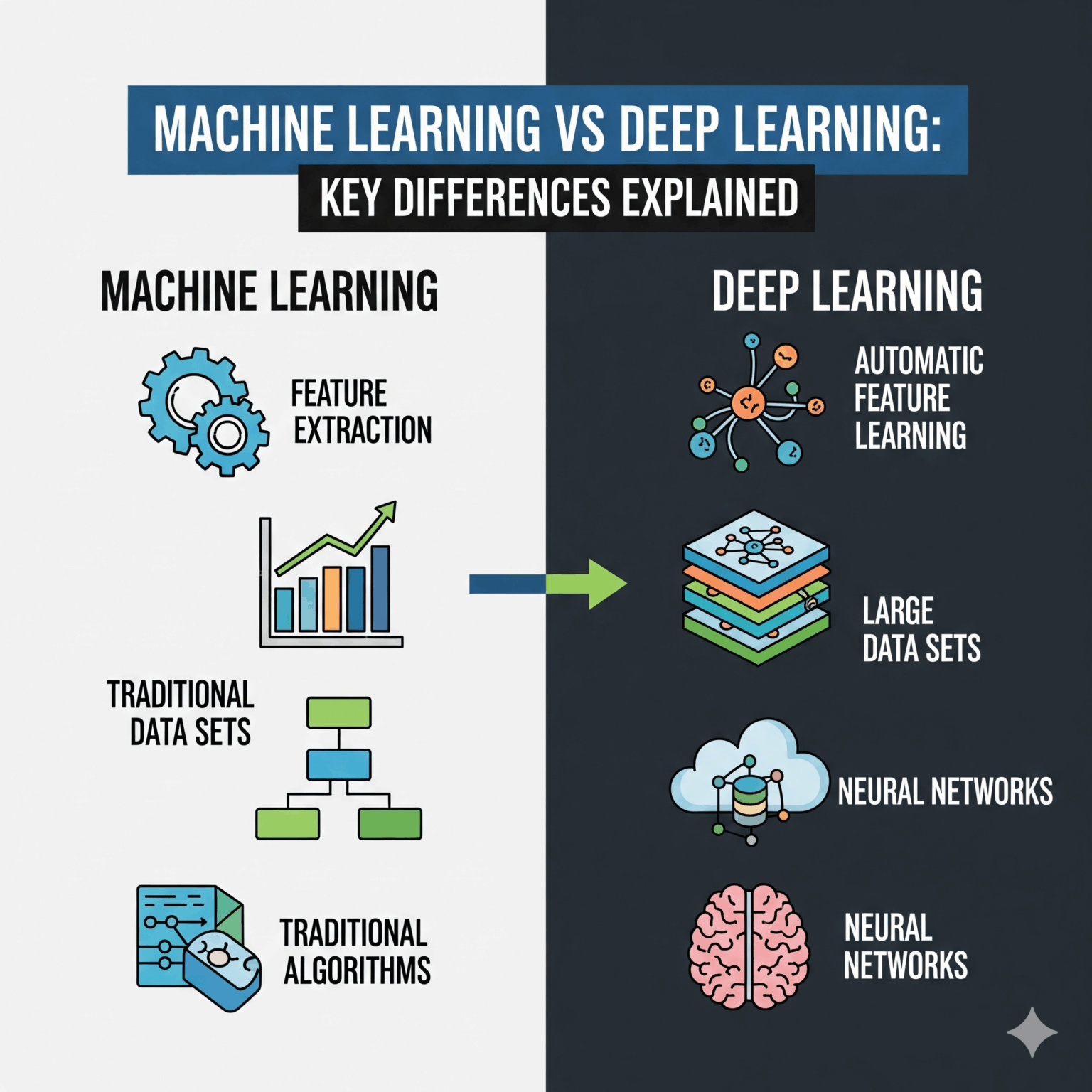
Machine learning is a subset of AI that enables systems to learn from data and improve their performance over time without being explicitly programmed. It uses algorithms to identify patterns, classify data, and make predictions. Examples include spam email detection, recommendation systems on e-commerce platforms, and fraud detection in banking. Machine learning typically requires structured data and works best with a manageable dataset.
What is Deep Learning?
Deep learning is a specialized branch of machine learning that uses artificial neural networks designed to mimic the human brain. It is capable of analyzing large amounts of unstructured data such as images, audio, and text. Deep learning powers technologies like voice assistants, self-driving cars, and advanced image recognition. Unlike traditional machine learning, deep learning models can automatically extract features from raw data, making them highly powerful but also resource-intensive.
Key Differences Between Machine Learning and Deep Learning
-
Data Requirements
Machine learning performs well with smaller datasets, while deep learning requires massive amounts of data to deliver accurate results. -
Hardware Dependence
Machine learning can run on standard computers, but deep learning often requires GPUs and advanced hardware to process complex neural networks. -
Feature Engineering
In machine learning, developers often need to manually select important features. Deep learning, however, learns features automatically through multiple network layers. -
Execution Time
Machine learning models are generally faster to train and test, whereas deep learning models may take hours or days due to their complexity. -
Applications
Machine learning is commonly used for recommendation engines, fraud detection, and predictive analytics. Deep learning is used in speech recognition, natural language processing, and computer vision.
Which One Should You Use?
The choice between machine learning and deep learning depends on your goals, resources, and the type of data you work with. For simpler problems with structured data, machine learning is efficient and cost-effective. If your project involves complex patterns such as image or voice recognition, deep learning is the better option despite its higher computing requirements.
Final Thoughts
Machine learning and deep learning are both essential to the growth of artificial intelligence. Machine learning provides practical solutions for data-driven decisions, while deep learning pushes the boundaries of what AI can achieve. By understanding their differences, businesses and developers can choose the right approach to harness the full potential of AI technologies.